Medication errors pose a significant challenge to the healthcare system in the United States, with the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) consistently receiving a staggering number of reports each year. This comprehensive analysis sheds light on key medication errors statistics, providing valuable insights into the magnitude of the issue.
Key Medication Errors Statistics
- The FDA records an alarming rate of medication errors, surpassing 100,000 reports annually, highlighting the pervasive nature of the problem within the U.S. healthcare system.
- A substantial 41% of U.S. citizens claim to have fallen victim to a medical error.
- Annually, over 7 million American patients experience some form of adverse effect due to medical errors.
- Outpatient clinics witness approximately 530,000 injury incidents annually as a direct result of medication errors.
- A concerning statistic reveals that 10% of patients within hospital settings are involved in medication errors.

What Are Medication Errors?
A medication error, also known as a medical error, occurs when there is an improper administration of healthcare to patients. These errors can manifest in various forms, such as administering pills in incorrect counts, at inappropriate dosages, or in the wrong quantities. It’s important to note that inaccuracies in entering drug information into a computer system also fall under the umbrella of medication errors.
| Medication Error | Error Rate (%) |
| Wrong Dose | 20 |
| Wrong Drug | 15 |
| Wrong Time | 10 |
| Wrong Route | 5 |
| Wrong Patient | 2 |
Medication errors are typically attributed to healthcare professionals directly involved in patient care, including doctors, nurses, and pharmacists. Any individual working with patients, administering treatments, or overseeing patient care is susceptible to being involved in the occurrence of medication errors.
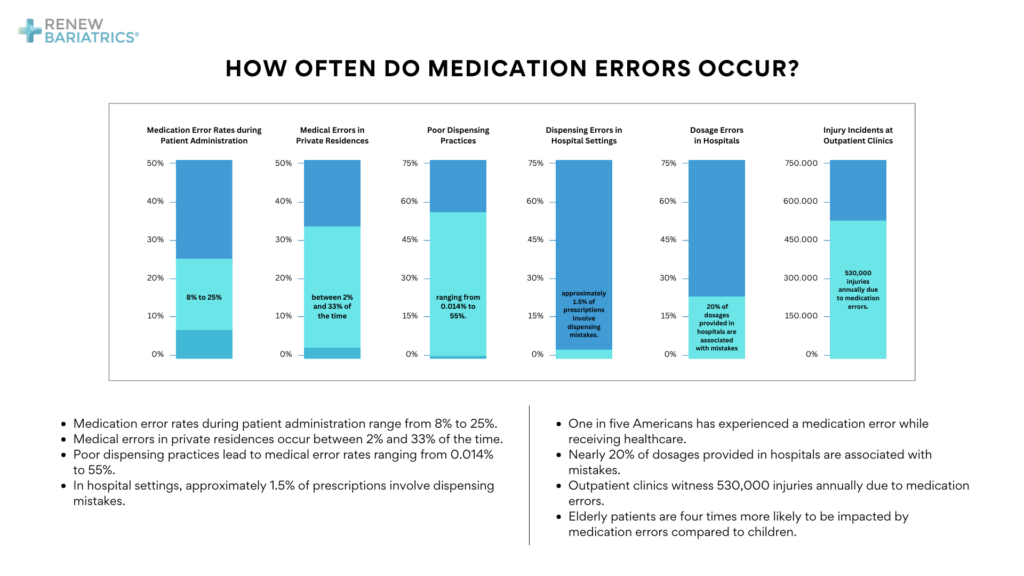
How Often Do Medication Errors Occur?
- Medication error rates during patient administration range from 8% to 25%.
- Medical errors in private residences occur between 2% and 33% of the time.
- Poor dispensing practices lead to medical error rates ranging from 0.014% to 55%.
- In hospital settings, approximately 1.5% of prescriptions involve dispensing mistakes.
- One in five Americans has experienced a medication error while receiving healthcare.
- Nearly 20% of dosages provided in hospitals are associated with mistakes.
- Outpatient clinics witness 530,000 injuries annually due to medication errors.
- Elderly patients are four times more likely to be impacted by medication errors compared to children.
Cost Of Medication Errors
- The United States allocates a substantial budget, exceeding $40 billion annually, to address the consequences of medical errors affecting patients.
- Preventable medication errors contribute significantly to this financial burden, accounting for over $21 billion in expenses each year. These errors are pervasive across the entire spectrum of the healthcare industry.
- The global cost attributed to medication errors represents nearly 1% of the entire worldwide expenditure on health.
Medication Error Mortality Rate
- Approximately 7,000 to 9,000 Americans pass away from medical errors annually.
- Medical errors claim a significant position as the eighth leading cause of mortality in the United States.
- Medication errors impact a staggering 1.3 million patients across the nation each year.
- On a daily basis, an average of one American loses their life due to becoming a victim of a medical error.
- Medical errors contribute to 30% of injuries resulting from prescribed medications within hospital environments.

What Are The Main Causes Of Medication Errors?
A comprehensive understanding of the various types of medication errors is crucial to address their root causes and pave the way for enhanced patient safety.
| Cause | Description | Common Causes |
| Administration | These errors occur during the actual administration of medication to patients. | Illegible writing on prescriptions. Mixing pills inappropriately. Administration by fatigued or allergic medical providers. |
| Prescribing | Mistakes made during the prescription process, including inadequate communication and documentation. | Illegible writing leading to misinterpretation. Prescription of incorrect dosage or medication. Lack of communication between healthcare professionals. |
| Communication | Failures in conveying accurate information between healthcare team members. | Ineffective communication channels. Misunderstandings in verbal or written instructions. Lack of clarity in prescription details. |
| Documentation | Mistakes in recording and maintaining patient medication information. | Incomplete or inaccurate documentation. Failure to update patient records promptly. Inadequate communication between healthcare providers and record keepers. |
| Ordering | Errors in the ordering or selection of medications for patients. | Confusion in selecting the right medication. Misinterpretation of patient history. System errors in the ordering process. |
FAQ
Which medication is most commonly associated with errors?
The frequently reported drug in instances of incorrect medication is OXYcodone with acetaminophen, commonly known as Percocet. This medication has often been mistakenly identified as HYDROcodone with acetaminophen (Vicodin, Norco), acetaminophen with codeine (Tylenol), and OXYcodone without acetaminophen.
Are medication errors entirely preventable?
While not entirely preventable, over 50% of harm is within the realm of prevention; half of this harm is linked to medications. Various estimates propose that as many as 4 in 10 patients experience harm in primary and ambulatory settings, with the potential to avert up to 80% (ranging from 23.6% to 85%) of this harm.
Who faces a higher risk of medication errors?
Patients with older age, multiple comorbidities, and those undergoing polypharmacy are at an elevated risk of experiencing medication errors, particularly in the context of chronic diseases.
References


