Gastric Balloon from $3,699
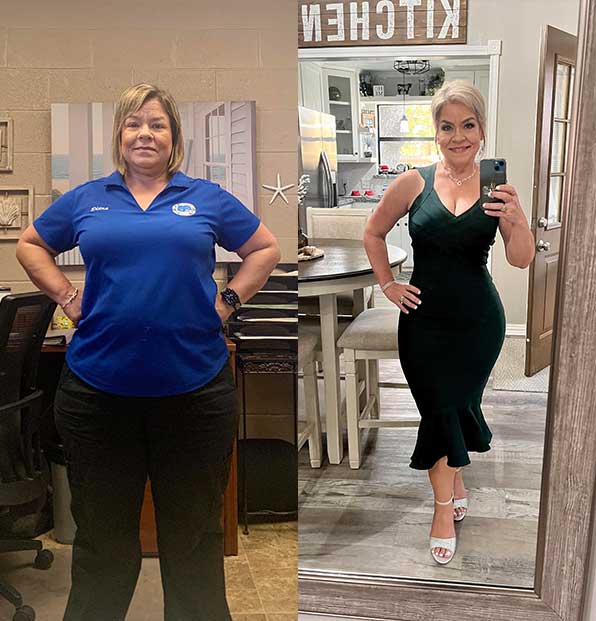
James
Lost 130 lbs


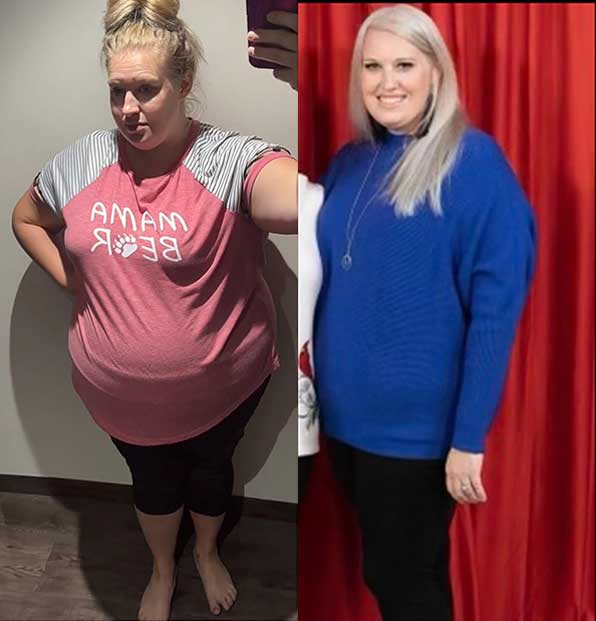
Autumn
Lost 210 lbs
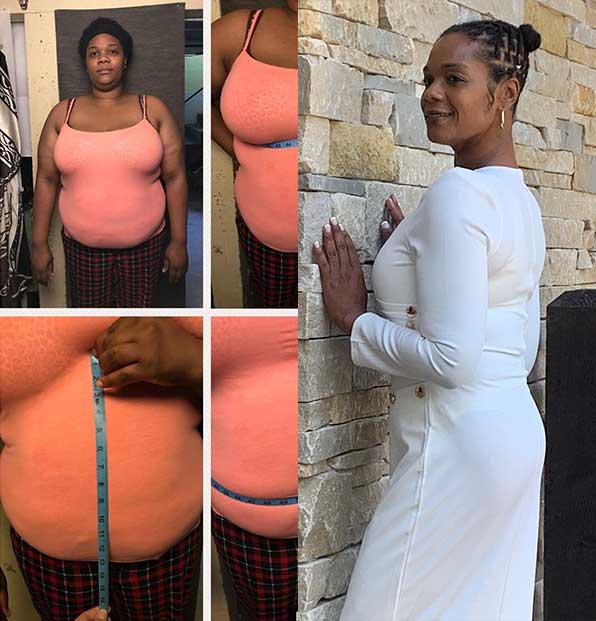
Felicia
Lost 107 lbs
Robbalee
Lost 270 lbs
A gastric balloon or intragastric balloon, is an inflatable medical device made of silicone placed in the stomach to achieve effective weight loss. It’s a form of non-surgical management of obesity. It has the advantage of being less invasive, temporary, reversible, cheaper, and is an outpatient procedure.
Gastric balloon systems use an inflatable balloon, usually saline or air, to restrict the stomach’s capacity, making the patient feel fuller and faster. The duration for most gastric balloons is typically 6 to 12 months. Learn more about the gastric balloon devices:
Many types of gastric balloons are currently used in endoscopic bariatric procedures. They include:
Also known as “ReShape Integrated Dual Balloon System”. The device is made of 2 balloons connected by a silicone shaft. The ReShape Duo Balloon System is an FDA-approved weight loss treatment, which is different by placing two interconnected balloons in the stomach endoscopically. Check Cost
This balloon is also swallowed and inflated with about 250 mL of air. Up to three oblong balloons can be placed in the stomach. It is the first and only swallowable balloon device approved by the FDA. However, at the end of 6 months, the balloons are deflated and removed by endoscopy. Check Cost
Though not FDA-approved, this balloon does not require endoscopy for placement. The balloon is swallowed like a tablet under fluoroscopy guidance and subsequently inflated with saline water via the tube that is attached to it. The balloon removal also does not need an endoscopy; the balloon spontaneously deflates after about 4 months and is subsequently excreted. Check Cost
Though yet to be approved by the FDA, it’s available in many countries, including Mexico. The Spatz Adjustable Balloon System is available for commercial use in over 32 countries. It is the only intragastric balloon device used for up to 12 months. Check Cost
It is the most frequently used and most studied intragastric balloon and was previously known as BioEnteric Intragastric Balloon (BIB). Orbera is an FDA-approved obesity treatment device that uses one balloon placed endoscopically to induce weight loss. Check Cost
The Heliosphere Bag is inserted by endoscopy but inflated with air. Compare the differences between gastric sleeve vs. gastric balloon. Renew Bariatrics recommends the gastric sleeve in Tijuana for long-term weight loss compared to the gastric balloon.
According to Kim et al., indications for gastric balloon are as follows:
Use the sliders to calculate your BMI and determine eligibility.
BMI
29
You are overweight
Use the weight loss calculator to see how much weight you could lose based on the surgery you select.
ReShape Duo Procedure
For obese patients not fit for bariatric (weight-reducing) surgery or those who want a non-invasive procedure, endoscopic intragastric balloon placement has been an option. This process is safe, reversible, and has fewer side effects and complications. Many devices are available for intragastric balloon placement. One such device is the ReShape Duo balloon. ReShape Duo, also known as “ReShape Integrated Dual Balloon System,” is one of the intragastric medical devices available for the endoscopic treatment of obesity. It was approved by the FDA on July 28, 2015 (“ReShape Integrated Dual Balloon System – P140012,” 2015).
As the name implies, the device comprises two balloons connected by a silicone shaft. The balloon is filled and sealed separately. The advantage of the two-balloon system is that if one ruptures, the other keeps it in place and prevents it from migrating down the bowel, causing an obstruction. The indications and contraindications for the ReShape Duo balloon apply to gastric balloons in general.
It is inserted into the stomach endoscopically under mild sedation. Once in place, the two balloons are inflated with about 900 mL of saline (salt water) mixed with methylene blue dye. The 900 mL of normal saline is equally distributed between the two balloons. The purpose of the methylene blue is to color the urine blue or green in case any balloon ruptures.

The way this device works is similar to that of other intragastric balloon devices. It occupies space in the stomach, leaving only a small space for food. This induces a feeling of fullness, leading to a decrease in food consumption and helping achieve weight loss goals. Another suggested method is by delaying gastric emptying.
After a 6-month stay, the endoscopy removes the balloon by aspirating the fluid.
Intragastric devices do not work independently. There is a need to strictly follow the dietary plan as prescribed by your doctor/nutritionist and to engage in appropriate physical activities if optimal weight reduction is to be achieved.
Some degree of discomfort may be experienced following the placement of the balloon, and some patients may experience nausea and vomiting within the first week of placement. Drinking excessive fluids can also worsen these symptoms.
Following the procedure, you will follow a liquid diet and exercise routine for a few days, gradually transitioning from liquids to semi-solid and solid foods.
On average, patients can expect to lose about 16.6kg following the placement of the ReShape Duo Double Balloon System, which equates to a 31.8% reduction in excess weight loss (EWL) at the 6-month mark after implantation. Additionally, 64% of the reduced body weight was maintained 12 months after the implantation (6 months after removal) (Kim et al., 2016).
The ReShape Integrated Dual Balloon System is a safe and effective endoscopic treatment for obesity, leading to considerable weight loss with minimal side effects.
Spatz Gastric Balloon
The endoscopic management of obesity is fast growing, with numerous intra-gastric balloon devices being developed. This modality of obesity management has been an option for obese patients who have failed to lose weight following a dietary and lifestyle adjustment and those who prefer a non-invasive procedure to bariatric surgeries.
Among the numerous intragastric balloons available for the endoscopic management of obesity, the Spatz Adjustable Balloon System has demonstrated effectiveness and minimal side effects.
Though yet to be approved by the FDA, the Spatz Adjustable Intragastric Balloon System is available for commercial use in over 32 countries, including Mexico. It is the only intragastric balloon device used for up to 12 months. It has the advantage of being adjustable, i.e., the saline quantity can be adjusted.
It is a silicone balloon inflated with saline (salt water). It includes a filling catheter, which is extractable endoscopically, that permits an intragastric balloon volume adjustment of 400-800 mL. The volume of the intragastric balloon may be modified to improve the patient’s tolerance and increase weight reduction (Kim et al., 2016).

In a 12-month pilot trial, 18 patients with a mean BMI of 37.3 Kg/m2 were implanted with the Spatz Adjustable Balloon System (ABS) for 12 months. The balloon volumes were adjusted for intolerance or plateau in weight loss measurement. Mean weight loss at six months post-implantation was 15.6 kg, with the percent of excess weight loss EWL of 26.4%. At 12 months post-implantation, the mean weight loss was 24.4 kg with a percentage EWL of 48.8% at 52 weeks (Machytka et al., 2011).
In another study conducted in the UK, the mean weight loss was 21.6 kg, while the percentage EWL was 45.7% (Brooks et al., 2014).
Orbera Gastric Balloon Procedure
Endoscopic treatment of obesity has become an option for patients who are not eligible for bariatric surgery. One such treatment is an intragastric balloon. Once placed in the stomach, the balloon is inflated, occupying about 80% of the stomach capacity, leaving only 20% for food. This leads to early satiety, reduced food intake, and subsequent weight loss. Another suggested method is to slow down the process of gastric emptying.
There are many types of gastric balloons. One of them is an Orbera balloon. It is the most frequently used intragastric balloon and was previously known as the BioEnteric Intragastric Balloon (BIB) (Kim et al., 2016). It is also the most studied intragastric balloon.
The FDA approved using the Orbera balloon on August 5, 2015. It is expected that the Orbera balloon could provide a valuable and less invasive therapeutic approach to bariatric treatment (Kim et al., 2016).
The indications and contraindications for the Orbera Gastric Balloon are similar to those for gastric balloons in general. Orbera balloons are made of silicone material. After placement, it is inflated with 450-700 mL of normal saline (salt water) mixed with methylene blue. If an unexpected balloon ruptures, the methylene blue turns the urine blue or green (Kim et al., 2016).
Interested in the Gastric Balloon Procedure? Contact our helpful patient educators today at Renew Bariatrics in Mexico to learn more about your options for weight loss surgery.
The balloon is inserted endoscopically under conscious sedation and removed after 6 months by the same endoscopic procedure.
Following the balloon placement, there may be some discomfort, and some patients may experience nausea and vomiting within the first week of placement. These can, however, be managed with appropriate medications.
Your doctor may place you on a liquid diet for a few days following Orbera balloon placement, gradually transitioning from liquid to semi-solid to solid foods. It is also important to adhere strictly to the dietary and lifestyle modification plans as prescribed by your doctor/nutritionist to ensure optimal weight loss.

Obalon Gastric Balloon Procedure

The FDA approved the Obalon balloon on September 8, 2016. It is the first and only swallowable balloon device approved by the FDA. The indication and contraindications for using Obalon are the same as for other intragastric balloons. This device has the added advantage of not requiring an endoscopy for placement like most other intragastric devices. It is swallowed like a capsule. The capsule is attached to a very thin catheter for inflation. Once in the stomach (as confirmed by fluoroscopy), the capsule dissolves, and the balloon is released. The balloon is then filled with 250 mL of air (unlike the usual saline used for most other intragastric devices), and the catheter is removed. Up to three different Obalons can be swallowed in a single session or placed one after the other within 6 months. The duration of stay of the Obalon is 6 months, after which the balloon(s) is/are removed by endoscopy. Side effects and complication profiles are similar to those of other gastric balloons. See “Gastric Balloon Complications” and “Gastric Balloon Side Effects” for more details.
In a pivotal study conducted in the US, where 185 patients underwent a combination of lifestyle modifications in addition to the Obalon, three balloons were inserted at contact, 3 weeks, and 9 or 12 weeks, respectively. The average percentage of total body weight loss (TBWL) at 6 months was 6.9%. The weight loss balloon seems well tolerated, with fewer accommodative symptoms than those observed with other fluid-filled balloons (Bazerbachi et al., 2017).
In a study conducted among obese pediatric patients, the average percentage of excess weight loss EWL after 18 weeks post balloon ingestion was 20.1% (De Peppo et al., 2017).
The gastric balloon takes is performed by the bariatrics surgeon endoscopically while under twilight sedation in this order:










Frequently asked questions by those interested gastric balloon in Mexico.
The best way to determine which bariatric surgery procedure is right for you is to discuss your options with your doctor. Your doctor will evaluate your health and weight loss goals to determine which type of bariatric surgery is the best fit.
The way the gastric balloon works is similar to restrictive bariatric procedures. When filled, the stomach balloon occupies roughly 80% of the stomach’s capacity, leaving just 20% for food. As a result, patients feel full even after consuming a small amount of food. This device can potentially reduce food intake and promote weight loss. However, like other bariatric procedures, it should be combined with dietary and lifestyle changes for effective results.
The deflated balloon is removed by endoscopy after 6 months post-insertion. This is done to prevent injury to the wall of the stomach and to avoid in-situ degradation of the balloon.

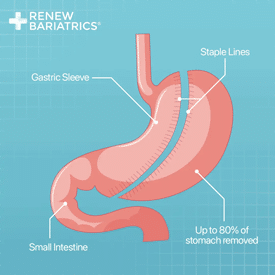
Gastric sleeve is the leading choice for those seeking to travel for their medical care. Gastric sleeve surgery provides the high expected weight loss and low risks. Gastric sleeve surgery is similar to gastric balloon, but is more invasive. Both utilize the same method of action to induce weight loss.
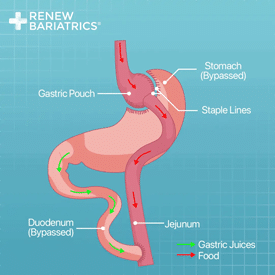
Gastric bypass is a leading option for those seeking a more invasive and powerful bariatric option. Gastric bypass surgery comes in various options Renew Bariatrics we provide: RNY Gastric Bypass Surgery and Mini Gastric Bypass Surgery.
Gastric balloon procedure is available at our hospital facilities in Tijuana. Weight loss surgery in Tijuana is a great option for those seeking a brief visit from San Diego in top tier medical facilities.
Gastric balloon procedure is available at our hospital facilities in Cancun, Mexico. Weight loss surgery in Cancun is a great option for those traveling from nearby, including gulf states like Flordia or Texas.
At Renew Bariatrics, we emphasize the principle of early satiety with the gastric balloon Tijuana providers offer, ensuring patients achieve their weight reduction goals. Renew Bariatrics has some of the best bariatric surgeons in Mexico who are dedicated to providing comprehensive care throughout their journey with the gastric balloon procedure.
Gastric balloon placement should be avoided in the following conditions.
Studies have shown that the average percentage of excess weight loss (EWL) after 6 months of balloon placement is 32%; however, by 1 year (6 months after removal of the balloon), the percentage of EWL was 10.9% (Ganesh et al., 2007). This is nevertheless significant as it has been discovered that a 10% reduction in excess body weight significantly reduces obesity-associated comorbidities (Evans & DeLegge, 2011).
In another study, the percentage of EWL after 1 year of insertion (6 months after removal) was found to be 14% to 50.9% (Kim et al., 2016). This wide variation in percentage EWL is due to the difference in the effectiveness of various types of gastric balloons.
The gastric balloon is one of the endoscopic weight loss treatments for obesity. It’s a safe and effective procedure that may serve as a bridge to bariatric surgery.
The major complications of the intragastric balloon are gastric ulcers, gastric erosion, esophagitis, spontaneous balloon deflation, and gastroesophageal reflux. There are also a few reported cases of gastric perforation, dilatation, and small intestinal obstruction (Coskun & Bozkurt, 2009).
Choosing the right surgeon for your weight-loss procedure is important. So, what makes Renew Bariatrics surgeons different?
Our surgeons have received training from some of the best medical institutions in the world. They have advanced English language skills. All of our surgeons are board-certified. They have helped thousands of patients like you achieve significant weight loss through gastric balloon.

Dr. Hector Joaquin Perez Corzo is a leading bariatric surgeon in Tijuana. Dr. Perez has more than 15 years of experience performing bariatric surgeries, especially the gastric balloon. He is board-certified and has trained at several world-renowned universities, including the University of Miami.

Dr. Green has more than 17 years of experience. He is board-certified in both bariatrics and general surgery. Always looking to provide the best care for his patients, Dr. Green will help you achieve your weight loss goals through weight loss surgery.

Board-certified in bariatric surgery, Dr. Rene Armenta is a leading bariatric surgeon. He has performed thousands of procedures on patients worldwide and is well-respected for his knowledge and expertise in bariatric medicine.

Dr. Antonio Cueva is a respected surgeon board-certified in general surgery and bariatrics. He has more than 18 years of experience in medicine and has performed hundreds of weight loss surgeries. Dr. Cueva is an empathetic surgeon who understands what patients are going through, as he has personally had gastric sleeve surgery himself.
Find your estimated weight loss after surgery.
Starting Weight
155 lbs
After 12-18 Months
155 lbs
Estimated Weight Loss
With you're estimated to lose 67 lbs over 12-18 months
You are currently below your ideal body weight and thus not a candidate for surgery.
Ideal Body Weight (IBW) represents the weight a person should be for their height. Excess Body Weight (EBW) is the amount of weight a person is over their IBW.
Ready to take the first step towards learning more about the gastric balloon surgery? Contact Renew Bariatrics at their Mexico locations today and let us them help you start your weight loss journey!
Copyright © 2024 Renew Bariatrics, Inc. – Proudly based in Mexico with offices in Tijuana and Cancun.
*Individual results may vary, please refer to our disclaimer page. This content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. This site complies with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information.
Renew Bariatric Doctors authored or reviewed and approved this content.