The duodenal switch also known as biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD-DS) is regarded as the most efficient, most complex and most complicated weight loss surgery. As a result, there has been a gradual decline in its performance as a treatment for obesity. It is now commonly done as a revision surgery when other operations have failed. Nevertheless, some morbidly obese patients may still want to choose it as a primary procedure. Gastric sleeve surgery used to be a component of BPD-DS, but it is now done as a stand-alone procedure for obesity. Both are effective in causing weight loss and improvement in obesity-associated conditions.
Renew Bariatrics recommends Gastric Sleeve Surgery for a majority of reasons, primarily that it provides sufficient expected weight loss, without high rates of complications or side effects.
Looking for top Gastric Sleeve Surgeons in Mexico? Contact us today learn more about our leading weight-loss surgeons and our results.
 |  |
|
|---|---|---|
| Gastric Sleeve Surgery | Duodenal Switch | |
| Method of Weight Loss | Restrictive | Restrictive & Malabsorptive |
| Duration of Procedure | 1.5 Hour | 4 Hour |
| Length of Hospital Stay | 2 Nights | 2-3 Nights |
| Estimated Weight Loss | 65% of Excess Weight | 65-90% of Excess Weight |
| Weight Loss at 1 Year | 60-70% | 70% |
| Comorbidities | High Resolved Rate | Significant Resolved Rates |
| Hypertension Resolved | 68% | 43% |
| Diabetes Resolved | 55% | 92-100% |
| Migrations Resolved | 40% | Major Improvements |
| GERD Resolved | 50% | 49% |
| Mortality | 0.1% | 0.3% |
| Asthma | 90% | 90% |
| Sleep Apnea | 62% | 85% |
| Depression | Most Resolved | 57% |
| Quality of Life Improved | 93% | 95% |
| Common Complications | Staple Line Leaks 0.5% | N/A |
| Common Side Effects | Nausea, Digestive Issues | GERD, Gallstone, Bowel Movement |
| Recovery | 2 to 4 Weeks | 2 to 4 Weeks |
| Cost: Self-Pay Average | $18,000 | $30,000 |
| Cost w/ Renew Bariatrics | $4,600 | $7,499 |
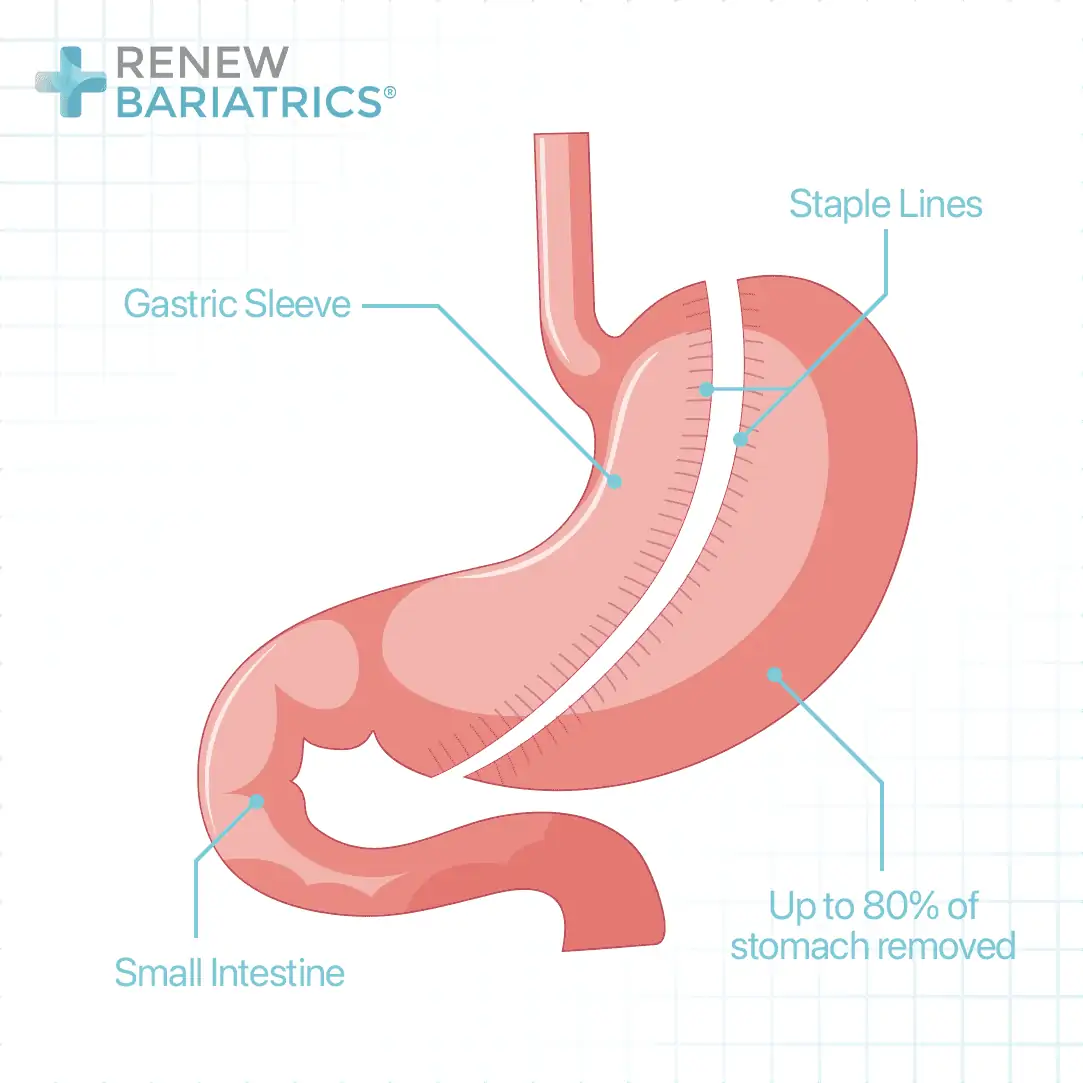
While gastric sleeve is purely restrictive, BPD-DS goes a step further to add a malabsorptive component to the mechanism of inducing weight loss. Gastric sleeve involves the reduction in the size of the stomach by resecting (cutting away) about 80-90% of it. This leads to an early feeling of fullness during the meal and therefore reduction in calorie intake.
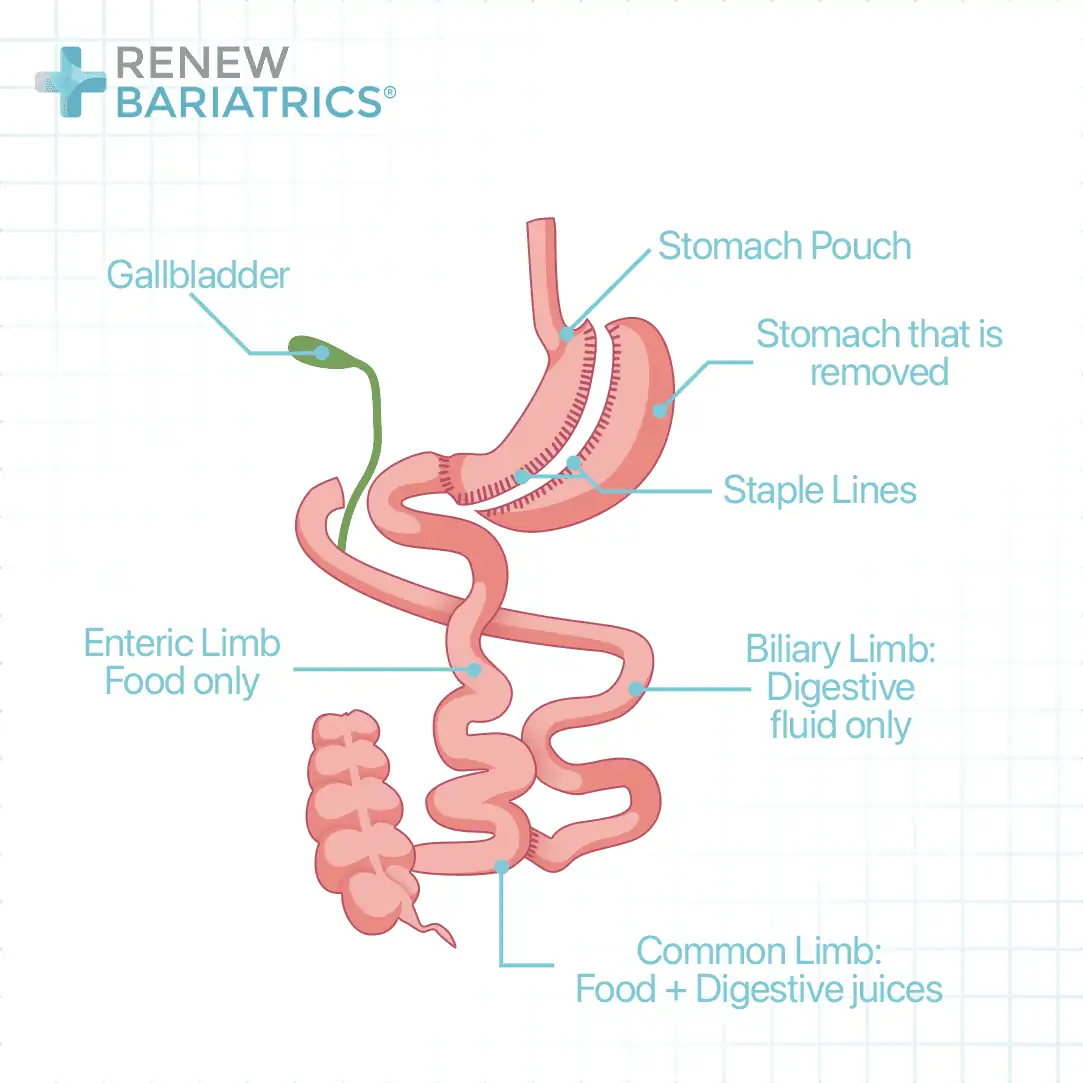
BPD-DS consists of gastric sleeve surgery with a malabsorptive component. The small intestine is refashioned in a way that allows the digestive enzymes from the pancreas and the bile to come in contact with the food at the lower end of the small intestine. As these digestive juices must act on the food before absorption can occur, most of the nutrients will not be absorbed.
Both gastric sleeve and BPD-DS can be done by laparoscopic (where equipment with the camera is introduced into the abdomen through small incisions) or open approach. The duration of surgery is more prolonged for BPD-DS (297min vs. 107min). The average length of hospital stay is also longer after BPD-DS by approximately one day.
Duodenal switch is more expensive than gastric sleeve surgery. The average cost of the duodenal switch in the United States is $25,000 ($23,000-$34,000) compared to the average price of gastric sleeve surgery of $15,000 ($12,000-$20,000). This is not unexpected as gastric sleeve surgery is one of the components of the duodenal switch. Cost is relatively lower outside the United States. While most insurance policies cover gastric sleeve surgery, only a few companies provide coverage for duodenal switch.
The expected weight loss, the improvement in obesity-associated disease conditions, the risk of complications and death are different for these two surgeries.
Duodenal switch results in a higher percentage of excess weight loss than gastric sleeve surgery. While patients are expected to have lost an average of 59% of the excess weight at 18-24 months after gastric sleeve surgery, the percentage excess weight loss after the duodenal switch is 78% with little weight regain even after 15 years of operation. Sucandy et al. reported a higher percentage excess weight loss at 18 months after duodenal switch (79.6% vs. 64%).
Due to the more significant weight loss that is associated with the duodenal switch, most patients tend to achieve a relatively lower body mass index (BMI) than their counterparts who underwent gastric sleeve surgery. Since lower BMI is associated with a higher resolution of comorbid conditions, it is therefore not surprising that more patients achieve reversal of their comorbidities such as type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, dyslipidemia, osteoarthritis, etc. after duodenal switch than after gastric sleeve surgery.
All the complications of gastric sleeve surgery occur after duodenal switch. Also, the duodenal switch also leads to other complications that are related to the manipulation of the small intestine. Common complications to both are leakage from staple line, gastroesophageal reflux disease, bleeding from the staple line, intra-abdominal abscess, stricture, hair loss, etc.
Those that are unique to duodenal switch are leakage from anastomotic sites, stricture at the anastomotic site, intestinal obstruction, ulcers, deep vein thrombosis (clotting of blood in the leg veins) with pulmonary embolism (obstruction of the blood vessels in the lungs by a blood clot), steatorrhea, etc. Nutritional deficiency is severe after duodenal switch. The risk of death after the duodenal switch is the highest among all bariatric surgeries and can be as high as 1.1%.
In summary, the comparison of different parameters of the duodenal switch and gastric sleeve surgery is shown in the table below:
Parameters | Duodenal switch (BPD-DS) | Gastric sleeve surgery |
Mechanism of weight loss | Restrictive and malabsorptive | Restrictive |
Duration of procedure | Shorter | |
Length of hospital stay | Shorter | |
Cost | Lower | |
Estimated weight loss | Higher | |
Reversal of comorbid conditions | Higher | |
Risk of complications | Lower (except heartburn) | |
Risk of death | Lower |
In conclusion, gastric sleeve surgery is a component of duodenal switch. It has, however, gained popularity as a stand-alone surgical procedure for the treatment obesity. It is less effective, when compared with duodenal switch, as regard weight loss and reversal of comorbid conditions, but cheaper and safer. Duodenal switch is now commonly done as a revision surgery after other bariatric surgeries have failed but can also be done as a primary procedure in super-obese individuals. It has the highest complication rates and risk of death.
Ready to move forward with affordable Weight Loss Surgery Mexico Tijuana with Renew Bariatrics? Contact us today learn more about your options.
Copyright © 2024 Renew Bariatrics, Inc. – Proudly based in Mexico with offices in Tijuana and Cancun.
*Individual results may vary, please refer to our disclaimer page. This content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. This site complies with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information.
Renew Bariatric Doctors authored or reviewed and approved this content.