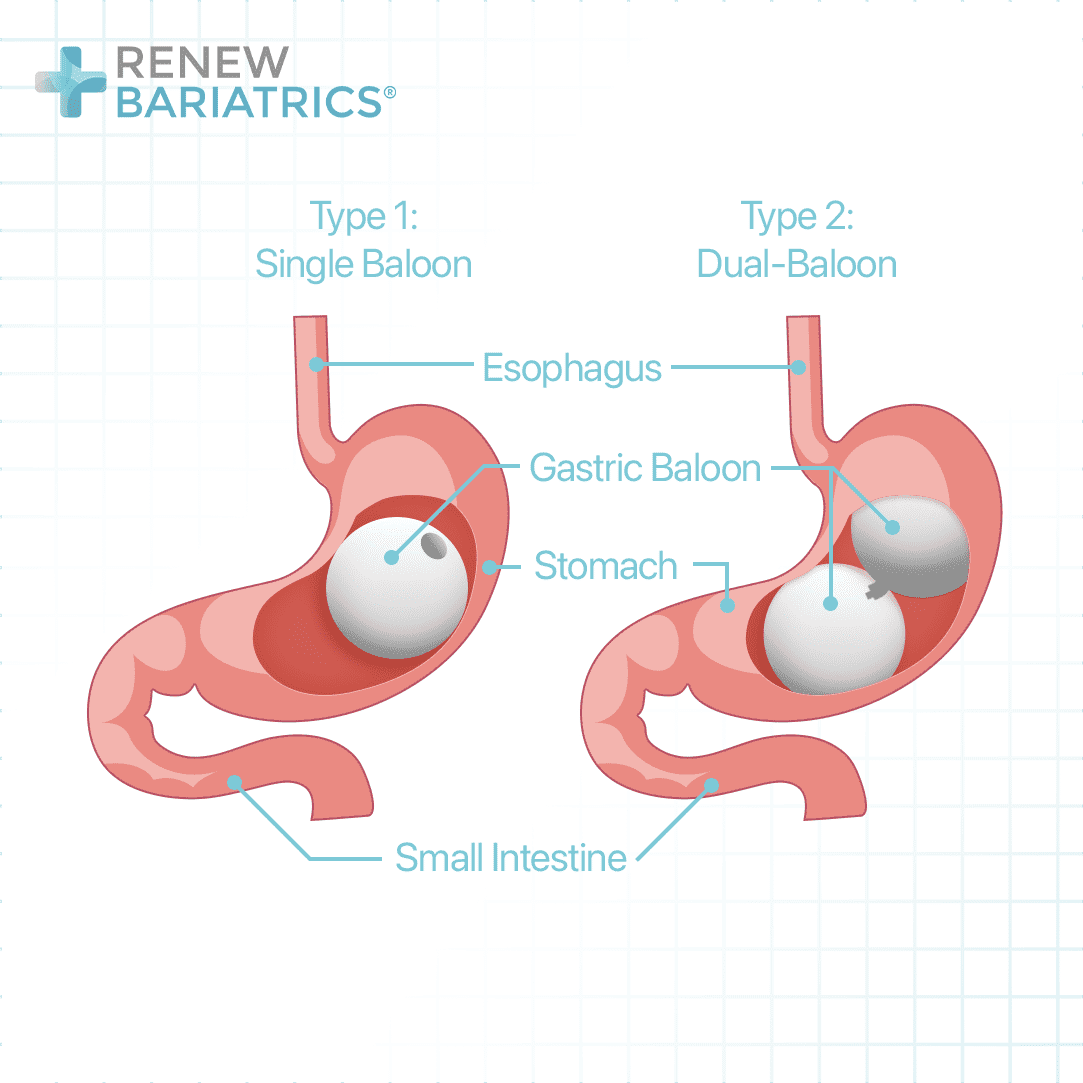
Weight loss surgeries are no doubt the most effective treatments for obesity, and gastric sleeve surgery is one of them. However, some obese individuals may not be fit for surgery or may not be willing to do surgery. Also, super obese people over 50 BMI tend to have a higher risk of complications following weight loss surgeries and therefore need to lose some weight before going for weight these surgeries. For this group of patients, intragastric balloon devices are the way out. There are many types of these balloons, but all of them perform the same function.
Renew Bariatrics recommends Gastric Sleeve Surgery for a majority of reasons, primarily that it provides sufficient expected weight loss. Also, because there lacks long-term data on the intragastric balloon.
Interested in undergoing the Sleeve Surgery in Mexico? Please contact our helpful, knowledgeable patient educators who can help guide you through the entire process of getting approved for the Gastric Sleeve Surgery.
 |  |
|
|---|---|---|
| Gastric Sleeve Surgery | Gastric Balloon Procedure | |
| Method of Weight Loss | Restrictive | Restrictive |
| Duration of Procedure | 1.5 Hour | 2 Hour |
| Length of Hospital Stay | 2 Nights | 0-1 Nights |
| Estimated Weight Loss | 65% of Excess Weight | 35% of Excess Weight |
| Weight Loss at 1 Year | 60-70% | 35% |
| Comorbidities | High Resolved Rate | N/A |
| Hypertension Resolved | 68% | N/A |
| Diabetes Resolved | 55% | N/A |
| Migrations Resolved | 40% | N/A |
| GERD Resolved | 50% | N/A |
| Mortality | ||
| Asthma | 90% | N/A |
| Sleep Apnea | 62% | N/A |
| Depression | Most Resolved | N/A |
| Quality of Life Improved | 93% | N/A |
| Common Complications | Staple Line Leaks 0.5% | N/A |
| Common Side Effects | ||
| Recovery | 2 to 4 Weeks | 1 Weeks |
| Cost: Self-Pay Average | $18,000 | $11,500 |
| Cost w/ Renew Bariatrics | $4,600 | $3,900 |
Both gastric sleeve surgery and the intragastric balloon cause weight loss by reducing the amount of calorie intake. This is made possible through a reduction in the capacity of the stomach. While this reduction is permanent for gastric sleeve surgery, it is temporary for gastric balloons. Most gastric balloons are deflated and removed after six months of placement to avoid complications.
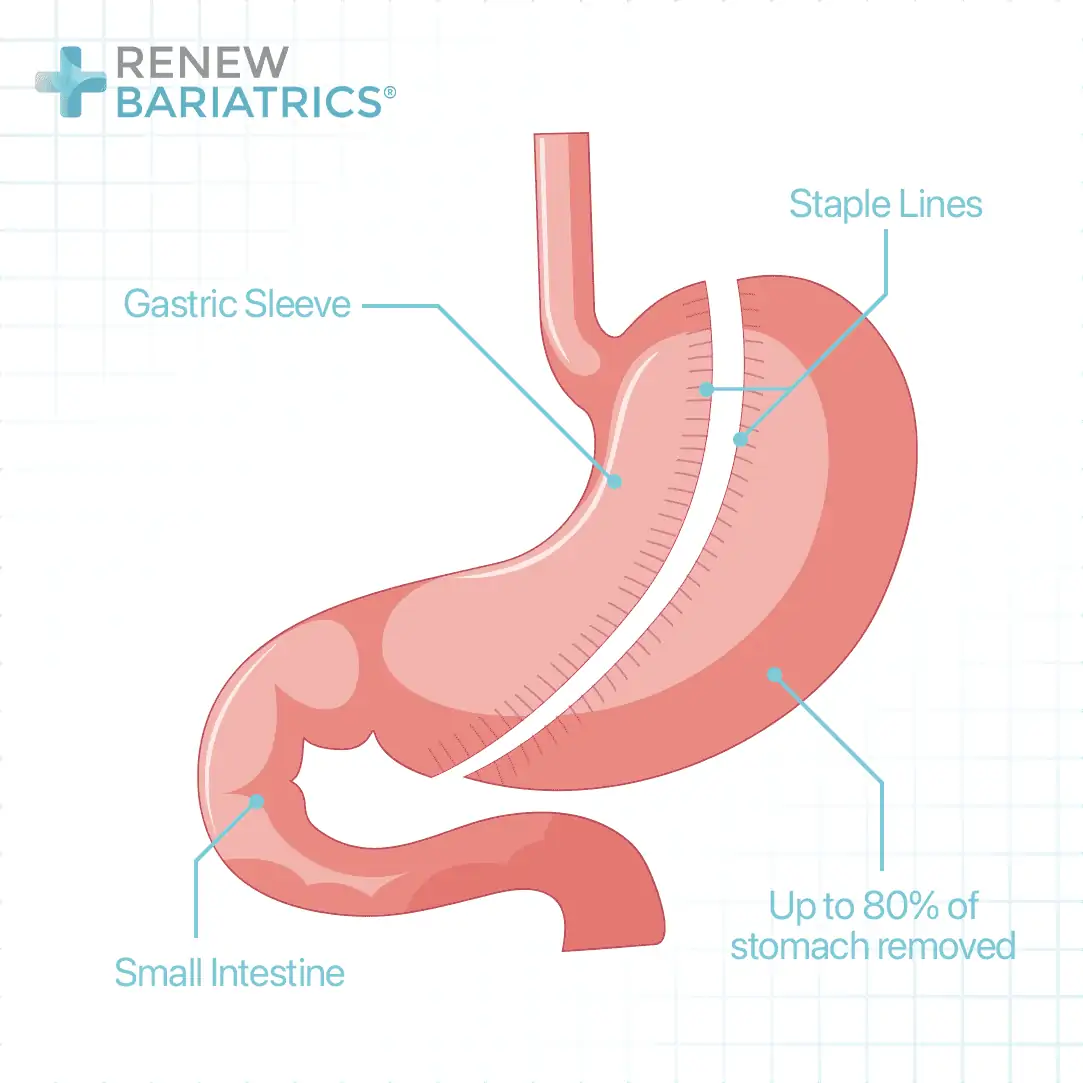
In gastric sleeve surgery, the stomach is resected (cutaway) to about 20% of its original size. This results in an early feeling of fullness during a meal with subsequent reduction in the quantity of food intake. There is also a decrease in the production of the hunger hormone, ghrelin leading to a decrease in appetite.
Gastric balloons are inflatable devices (made of silicone) that are inserted into the stomach and subsequently inflated by either water or air. They occupy space within the stomach and therefore cause an early sensation of fullness during a meal.

Gastric sleeve surgery is done by a laparoscopic approach where small incisions are made in the abdomen and equipment with the camera is introduced into the abdominal cavity. It can also be done by open surgery. Gastric balloons, on the other hand, are inserted into and also removed from the stomach by endoscopy. Endoscopy involves the passage of a flexible tube with a camera into the stomach via the mouth. Exceptions to this are the obalon and the elipse devices that are swallowed. The duration of gastric sleeve surgery is approximately 100min. While that of gastric balloon insertion is less than 30min.
The average cost of gastric sleeve surgery is $15,000 ($12,000-$20,000) in the United States. Gastric balloon cost also varies from one country to another, based on the hospital and the type of balloon. In the U.S. the cost ranges from $3,000 to $9,000. Most insurance companies provide coverage for gastric sleeve surgery while only few insurance policies cover gastric balloon as their approval is still recent in the U.S.
On an average, a patient would have lost up to 50% of the excess weight by 6 months after gastric sleeve surgery. This is higher than after gastric balloon placement where the average percentage excess weight loss is about 32% reducing to 10.9% at 12 months (6months after balloon removal).
As gastric sleeve surgery results in more weight loss, resolution of obesity-associated disease conditions is higher after gastric sleeve surgery than after gastric balloon placement. This may not be unconnected to the fact that gastric balloon is only left in the stomach for just 6months. A much lower improvement in comorbid conditions has been recorded in gastric balloon patients. reported a reduction in the incidence of the type of diabetes mellitus from 32.6% to 20.9%, hypertension from 44.9% to 30.4%, at 6months after gastric balloon placement, all of which are lower compared to gastric sleeve surgery.
More complications are associated with gastric sleeve surgery than with gastric balloon. Complications of gastric sleeve surgery are those of anesthesia, and the surgery itself. These include leakage from staple line, intra-abdominal bleeding/abscess, heartburn, etc. The gastric balloon, on the other hand, has minimal complications most of which often occurs if the balloon is left beyond 6months. Some of these are gastric erosion/ulcers, spontaneous balloon deflation with subsequent migration to cause small intestinal obstruction and heartburn from gastroesophageal reflux.
In summary, the comparison between gastric sleeve surgery and the gastric balloon is shown in the table below:
Parameters | Gastric sleeve surgery | Gastric balloon |
Mechanism of weight loss | Restrictive | Restrictive |
Reversibility | Impossible | Possible |
Duration of procedure | Shorter | |
Length of hospital stay | Shorter | |
Cost | Lower | |
Insurance coverage | Yes | Yes/No |
Estimated weight loss | Higher | |
Reversal of comorbid conditions | Higher | |
Risk of complications | Lower | |
Risk of death | Negligible | Negligible |
In conclusion, gastric balloon is a temporary, non-surgical weight loss procedure meant for super obese individuals before surgery or those that are not fit for surgery. Most are only left in the stomach for six months. They offer a lesser degree of weight loss and reversal of comorbid conditions when compared to gastric sleeve surgery, but they are cheaper, easier, reversible, and associated with fewer complications.
Copyright © 2023 Renew Bariatrics, Inc.
“Individual results are not guaranteed and may vary, please refer to our disclaimer page. This content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or another qualified health provider.”
“Renew Bariatrics, Inc. is a medical tourism scheduling facilitator, not a healthcare provider.”